BigData World
What is Big data?
Big data is also data but with an immense scale. Big Data is a concept used to characterize a data set that is immense in volume and yet exponentially increasing over time.
In short, such data is so huge and complex that it can not be saved or processed effectively by any of the conventional data processing methods. The concept of Big Data gained traction in early 2000’s when industry analyst Doug Laney expressed the now-mainstream idea of big data as the three V’s.
The three V’s
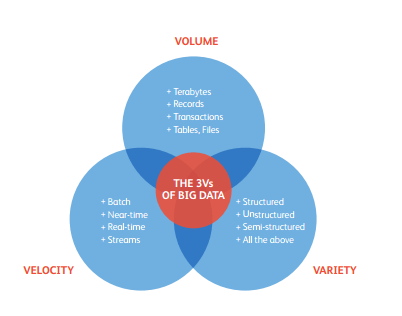
Volume :- Organizations gather data from a variety of sources including business transactions, smart devices, social media and more. Storing it may have been a challenge in the past-but cheaper storage on platforms such as data lakes and Hadoop has eased the burden.
Velocity :- With the growth of the Internet of Things, data flows at an incredible pace to companies and must be managed in a timely manner. The need to deal with these streams of information in real time is powered by RFID tags, sensors and smart meters.
Variety :- Data comes in all sorts of formats, from structured, numerical data to unstructured text documents, emails, images, audios and financial transactions in conventional databases.
Need of Big Data
According to an IBM Marketing Cloud report, 90 % of the data on the internet have been generated since 2016. People, companies, and computers have all become factories of data that pump enormous amounts of information into the web every day. You might be surprised to find out that :-
- 1.7MB of data is created every second by every person during 2020.
- There are 4.57 billion active internet users around the world
- 2.5 quintillion bytes of data are produced by humans every day.
- 463 exabytes of data will be generated each day by humans as of 2025.
- 95 million photos and videos are shared every day on Instagram.
- By the end of 2020, 44 zettabytes will make up the entire digital universe.
- Every day, 306.4 billion emails are sent, and 5 million Tweets are made.
- 350 million photos are uploaded to Facebook each day.
How big tech companies managing this huge amount of data?
Companies like Google,Yahoo, Facebook, Microsoft and others started to work upon big data and all the data related issues are being solved using Hadoop and big data insights.
Earlier, all businesses were using RDBMS to store their data in which we can read once and write N number of times that are not applicable to a large amount of data being read. So Doug Cutting came up with a solution like Hadoop that is based to work on enormous data in distributed and parallel fashion. In Hadoop we can write once and read N number of times, HDFS is used to store data in cluster (group of nodes) and we can process the data accordingly to the need of the company using Map-Reduce. Data sorting, filtering, partitioning and bucketing are done to calculate the outcome. This is the company’s modern and precise way of using its results.
How Hadoop is solving Big Data problem?


It is build to run on cluster of machines. Let ‘s begin with an example. Let ‘s say there are tons of images we need to store. We’re going to start with a single disc. When we exceed a single disk, we will use a few disks stacked on a computer. When we max out all the disks on a single computer, we need to get a bunch of computers, each with a bunch of disks.
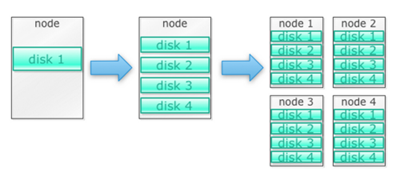
By adding more nodes to a Hadoop cluster, more storage and computing power can be achieved. This eliminates the need to purchase more and more better and more costly hardware.
Hadoop is designed to handle the three V’s of Big Data: volume, variety, velocity. First lets look at volume, Hadoop is a distributed architecture that scales cost effectively. In other words, Hadoop was designed to scale out, and it is much more cost effective to grow the system. As you need more storage or computing capacity, all you need to do is add more nodes to the cluster. Second is variety, Hadoop allows you to store data in any format, be that structured or unstructured data. This means that you will not need to alter your data to fit any single schema before putting it into Hadoop. Next is velocity, with Hadoop you can load raw data into the system and then later define how you want to view it. Because of the flexibility of the system, you are able to avoid many network and processing bottlenecks associated with loading raw data. Since data is always changing, the flexibility of the system makes it much easier to integrate any changes.
Big data can be expensive to store using conventional storage. Hadoop is designed around commodity hardware, so for a reasonable cost, it can provide fairly large storage. Hadoop has been used in the field at petabyte scale. One study by Cloudera suggested that businesses normally spend around $25,000 to $50,000 per terabyte per year. This expense decreases to a couple of thousand dollars per terabyte per year with Hadoop. This cost continues to decline as hardware gets cheaper and cheaper.
There is no point in keeping all this data unless we can analyze it. Not only does Hadoop have distributed storage, but also distributed processing, which ensures that a huge amount of data can be crunched in parallel. Hadoop’s compute framework is known as MapReduce. MapReduce has been proven to the scale of petabytes.


Organizations begin to utilize Hadoop when they need faster processing on large data sets. Large users of Hadoop include: Facebook, Amazon, Adobe, EBay, and LinkedIn. It is also in use throughout the financial sector and the US government. These organizations are a testament to what can be done at internet speed by utilizing big data to its fullest extent
